Last Updated on: 29th noviembre 2025, 07:50 am
[ux_text text_color=»rgb(0,0,0)»]
Oral health is an essential component of our overall health. Despite its importance, oral diseases, especially those related to the gums, are common in populations of all ages. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is one of the most prevalent oral problems in today’s society. This condition can range in severity from simple gingival inflammation to advanced disease affecting the tissue that supports the teeth. Given its importance, it is essential to have a complete understanding of its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
In this article, we take a deep dive into gum disease, its symptoms, risk factors, and how up-to-date information can help in its prevention and treatment. Let’s find out!
Global Context and Current Events
The World Health Organization has noted that oral diseases have increased in prevalence over the past decade, affecting an estimated 3.5 billion people. Advances in dental research and technology have led to better understanding and treatment, but prevention remains essential. This burden of disease can be costly and, in many countries, is not covered by public health care.
Prevalence in the US
The situation in the United States is alarming. The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research suggests that many adults suffer from gum disease. These diseases range from simple inflammation to serious conditions that can lead to tooth loss.
What is gum disease?
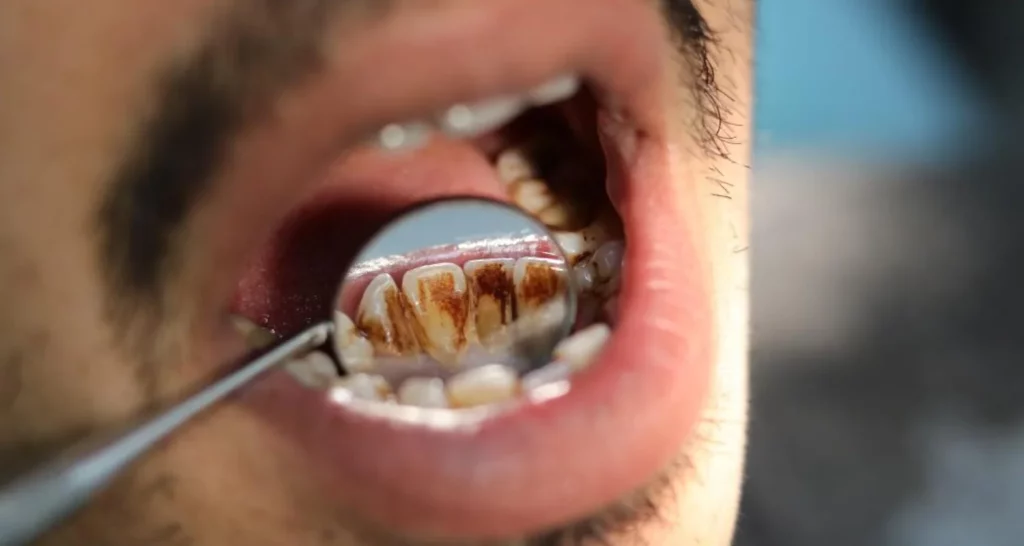
Gum disease, or periodontitis, refers to inflammation and infection that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It occurs when bacteria in plaque (a sticky film that forms on teeth) produce substances that inflame and irritate the gums. If this condition persists, the gums can pull away from the teeth, forming bacteria-filled pockets that further infect the periodontal tissue.
Gingivitis and periodontitis
There are different stages in the evolution of this disease, with gingivitis being the most common and treatable. However, without proper care, it can evolve into periodontitis , a stage with more severe and, unfortunately, irreversible consequences.
Gum disease has two main forms: gingivitis and periodontitis. While gingivitis is a mild infection of the gums, periodontitis is an advanced and more damaging version. If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, leading to more serious damage and tooth loss.
Gum Disease and General Health
Recent research has shown that gum disease may be linked to heart problems, diabetes, and premature birth. Bacteria present in inflamed gums can enter the bloodstream, affecting other organs and systems. This two-way relationship means that, on the one hand, having periodontal disease can increase the risk of suffering from other diseases, and on the other, certain systemic diseases can increase the likelihood of developing gum problems.
Risk factors
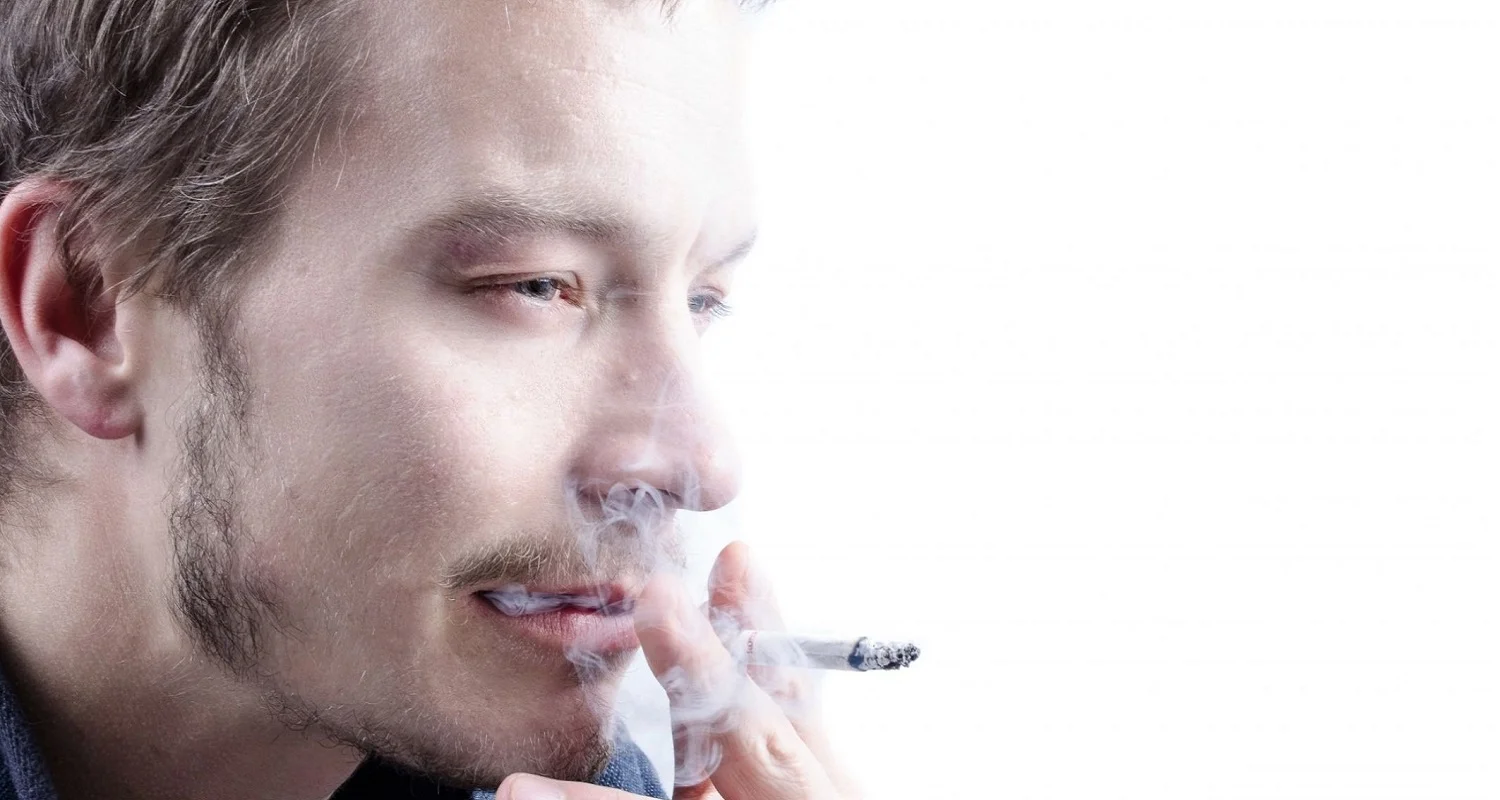
Certain individuals are more likely to develop gum disease due to their habits, genetics, or medical conditions. These include smokers, people with high stress levels, and those with a family history of gum disease.
Internal and external factors: From hormonal changes to medications, several factors can increase the risk of gum disease. In addition, diseases that compromise the immune system, such as HIV or lupus, can increase susceptibility to oral infections.
Likewise, plaque buildup is the main cause of gum disease, but there are other risk factors that promote it:
- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly increases your risk.
- Smoking: It is one of the main factors in the development of gum disease.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, puberty and menopause can make gums more sensitive.
- Systemic diseases: Diabetes, heart disease, and cancer can increase the likelihood of gingival inflammation.
- Medications: Some reduce salivary flow, decreasing natural protection against bacteria.

Habits and diseases
People with diabetes, heart disease, or immune disorders are also at increased risk. Poor oral hygiene, missed visits to the dentist, and having crooked or misaligned teeth are other factors to consider. If you’re interested in learning about crooked teeth in babies, feel free to check out our article here .
Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
Identifying gum disease early is crucial for effective treatment. These are the symptoms to look out for:
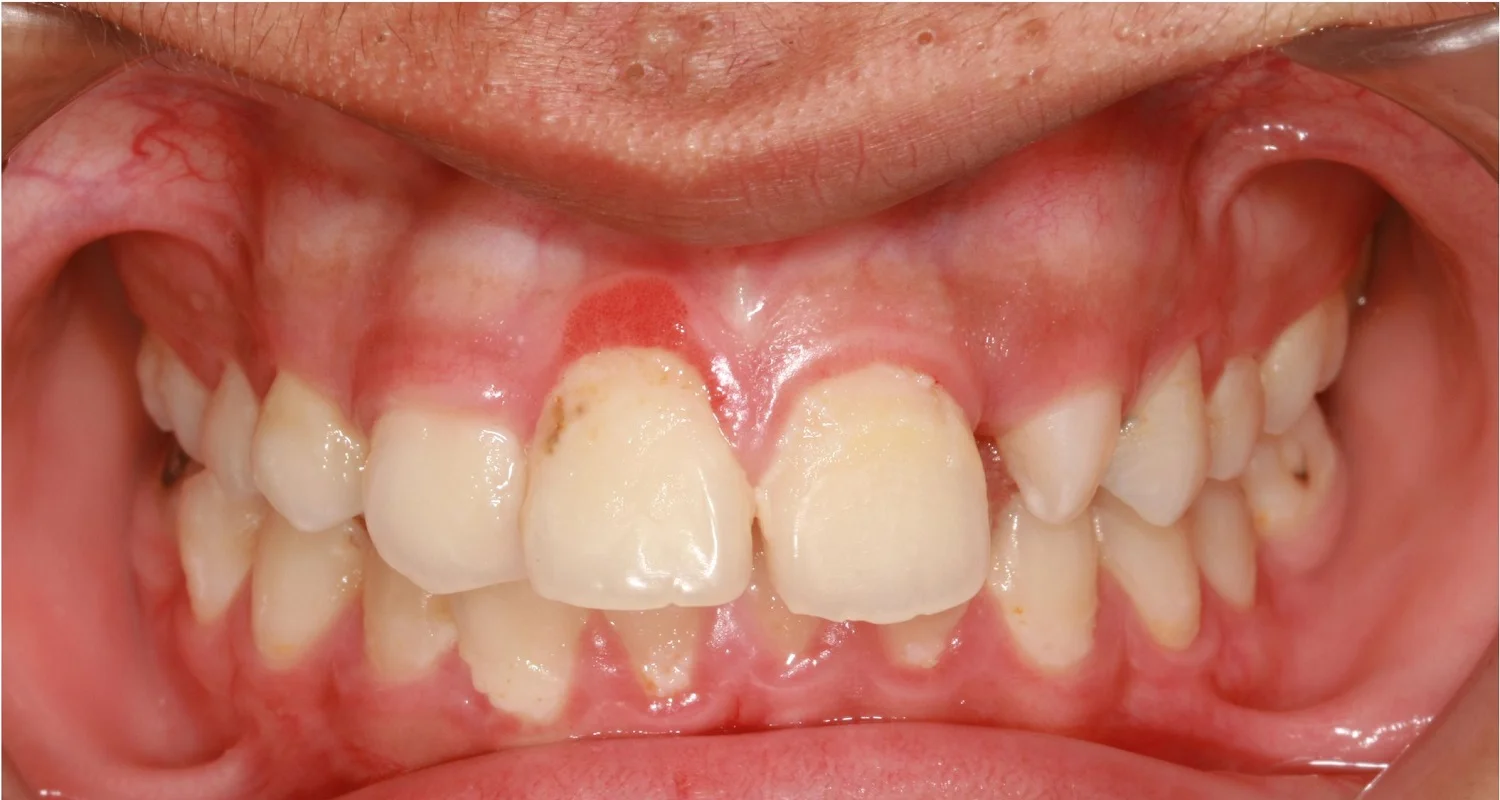
- Red, swollen or bleeding gums.
- Gingival recession, where the gums move away from the teeth.
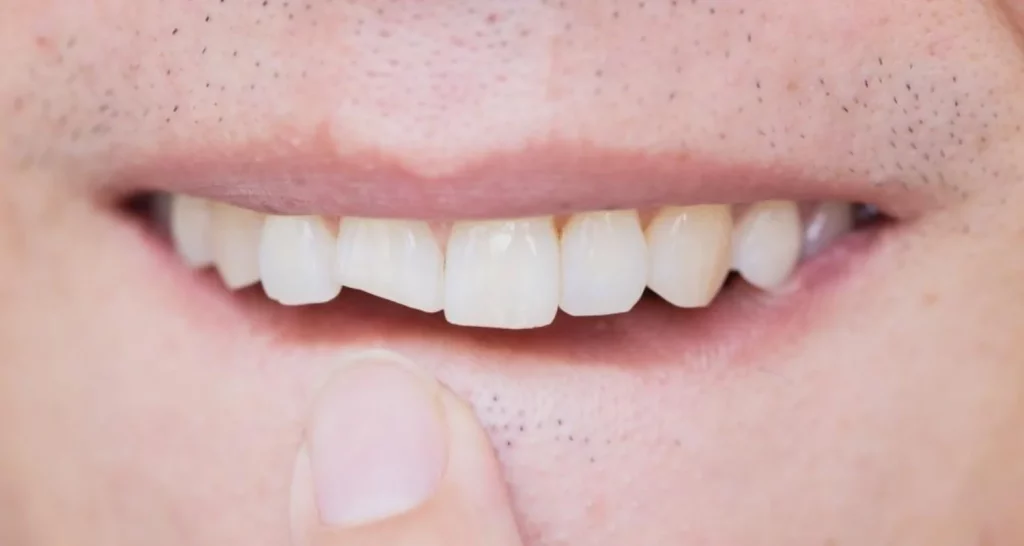
- Loose teeth.
- Pus between teeth and gums.
- Pain when chewing.
- Dental sensitivity.

It is crucial to be aware of the early symptoms: red, swollen gums, bleeding when brushing, persistent bad breath, receding gums and tooth sensitivity. Recognizing these signs early can be the key to successful treatment.
Advanced gum disease can lead to receding gums, sensitive teeth, and eventually loose or shifting teeth. It is essential to understand how this affects our overall oral health and act accordingly.
Role of plaque and dental hygiene
Dental plaque plays a central role in gum disease. This sticky, bacteria-filled film builds up on teeth and, if not removed, can irritate the gums. Proper oral hygiene is therefore essential to prevent its formation and buildup.
Treatment and diagnosis of gum disease
Early diagnosis of gum disease is key. Thanks to today’s technology, we have tools such as digital x-rays and genetic testing that can identify predispositions to the disease and detect it in its early stages.
Treatments have evolved, including less invasive therapies such as curettage and root planing, localized administration of antimicrobials and, in advanced cases, regenerative therapies with biocompatible materials.
Some of these are:
- Professional Cleaning: In the early stages of the disease, a professional dental cleaning may be sufficient. This procedure removes plaque and tartar from the tooth surface and below the gum line.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This is a more thorough procedure than conventional cleaning. The dentist scales and smoothes the roots of the teeth to remove bacteria and provide a clean surface for the gums to re-attach.
- Periodontal Surgery: In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary to clean out pockets of infection and reshape damaged bone.
- Medications: There are topical and oral medications that can be prescribed to control the infection and reduce the size of periodontal pockets.
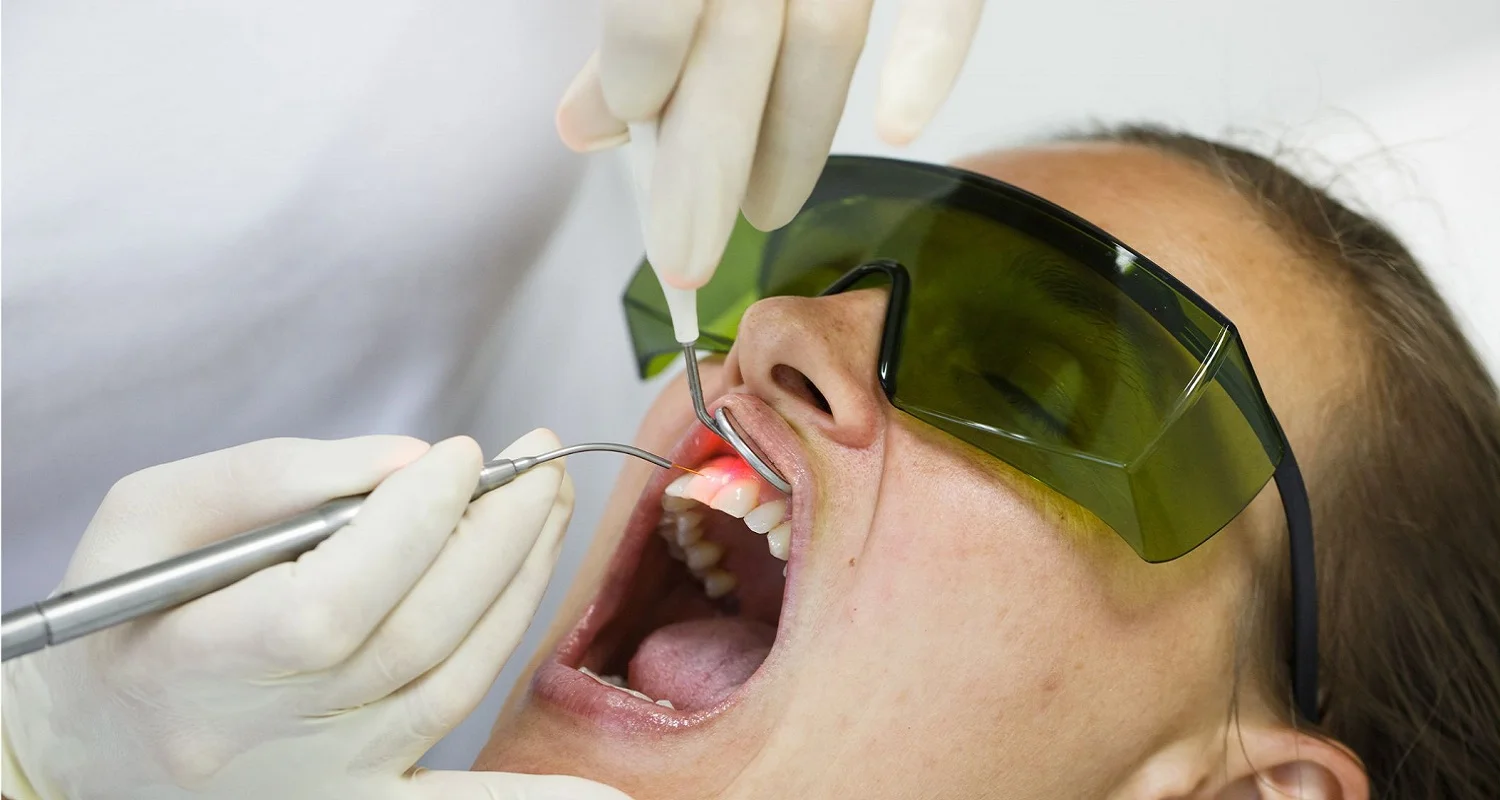
- Laser therapy: A less invasive treatment that uses laser light to remove inflamed and damaged tissue.
Natural and home treatment
To alleviate a gum infection, it is essential to follow an unwritten rule that most people know: to preserve oral health, it is essential to have at least two dental cleanings per year with a specialist. The accumulation of tartar and bacterial plaque is often the root of gum infections, and this requires professional intervention.
In addition, natural and home remedies are often highly effective and are even recommended by dentists. Using these homemade treatments on a daily basis can provide significant and long-lasting relief.
1. Use of mouthwashes
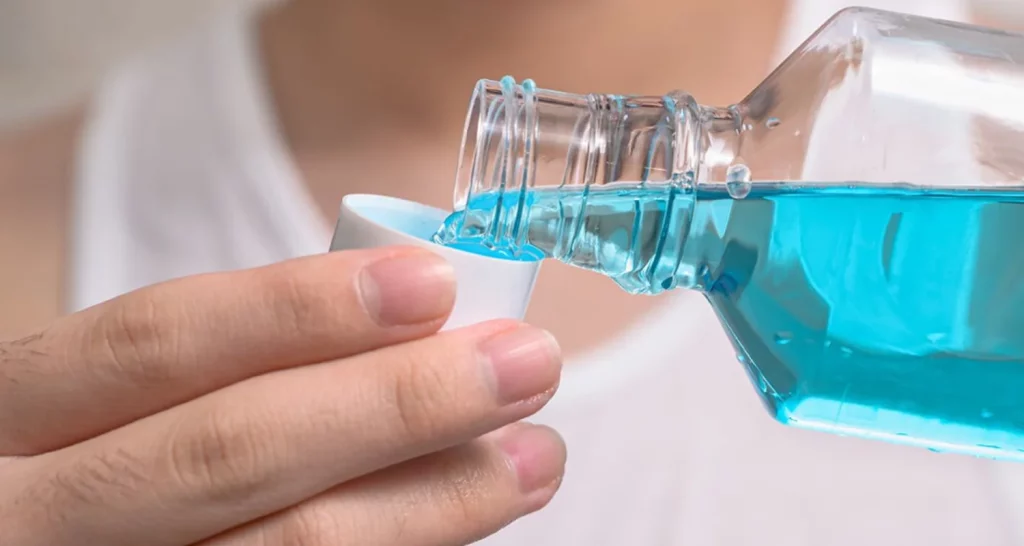

The main purpose of mouthwashes is to fight dental plaque, responsible for gum diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis, according to a study by the Complutense University of Madrid.
Therefore, one of the most effective home remedies to combat plaque is the use of mouthwash. Below, we explain how to prepare it.
Ingredients
- 2 tablespoons of mouthwash (30 ml)
- 1 tablespoon of water (15 ml)
- Salt (optional)
Instructions
- Mix a small amount of mouthwash with a few drops of water, making sure that it is not in equal proportions.
- To intensify the mixture, you can add a pinch of salt.
- Once the ingredients are combined, gargle with the mixture, ideally after each meal.
2. Lemon juice

Lemon, thanks to its anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, can be effective in relieving gingivitis. Its acidity prevents the proliferation of bacteria and balances oral pH, also helping to combat bad breath.
Procedure:
- Squeeze the juice of half a lemon and mix it with a cup of warm water.
- Use this solution to rinse your mouth, avoiding swallowing.
- Use this mouthwash twice a day, but limit its use to specific, non-prolonged treatments, since the acid in lemon can damage tooth enamel.
3. Chamomile infusion

Chamomile is known for its anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and analgesic properties, as well as promoting the healing of inflamed gums by stimulating blood circulation and reducing swelling.
This herb also has a soothing and disinfecting effect on inflamed gums. Prepare a chamomile infusion by letting it sit for 5 minutes and use it to rinse your mouth several times a day.
4. Coconut Oil Mouthwash (Oil Pulling Technique)
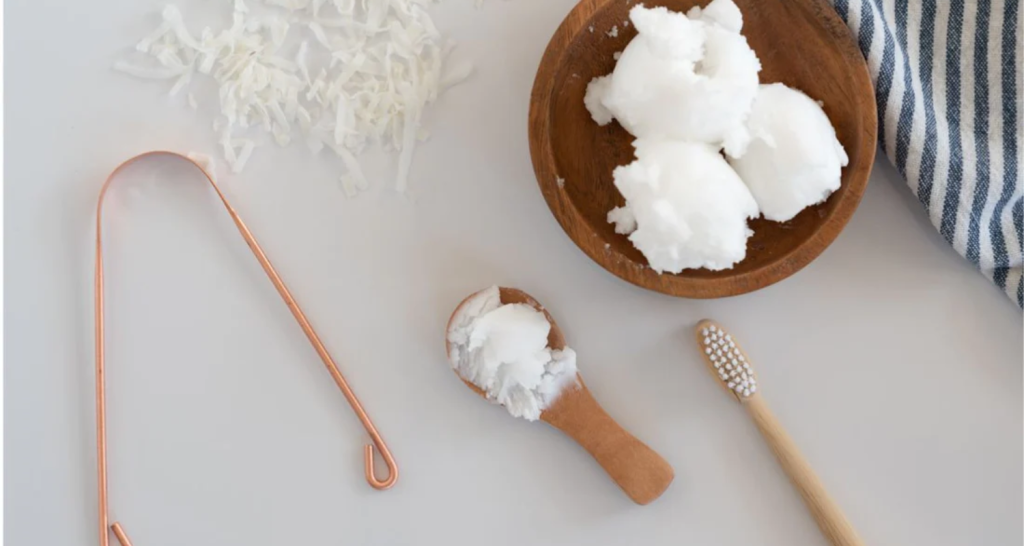

Coconut oil contains lauric acid, which is useful in fighting bacteria and pathogens. To combat or prevent gum inflammation:
- Take a teaspoon of coconut oil and allow it to dissolve in your mouth.
- Actively move the oil back and forth in your mouth, passing it between your teeth, for five to ten minutes. This ensures that it reaches all areas of your teeth.
This technique, known as «oil pulling», is recommended to be performed daily or at least twice a week.
5. Aloe Vera Extract
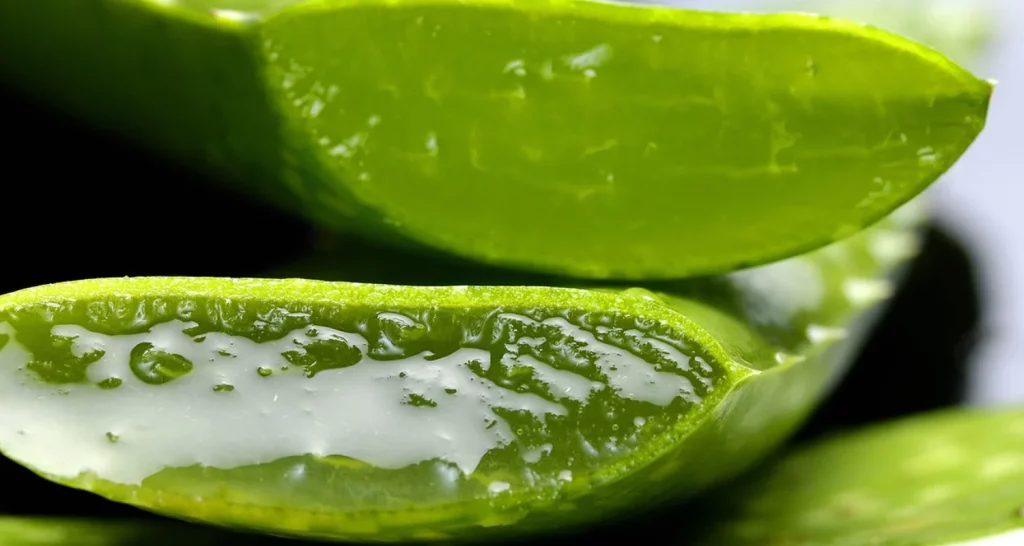

Aloe vera is known for its anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, soothing and healing properties, which are beneficial in treating gum infections, including gingivitis and periodontitis. Interestingly, toothpastes containing aloe vera are effective in inhibiting the growth of microorganisms in the mouth.
Ingredients
- Two aloe vera leaves.
- 150 ml of water.
- A teaspoon of honey (optional).
Instructions
- Extract the aloe vera pulp and blend it in a blender with the other ingredients. You can add more water to dilute the mixture if you prefer. Store the remaining amount in the refrigerator.
- Use this juice as a mouthwash twice a day.
6. Watercress Rinse
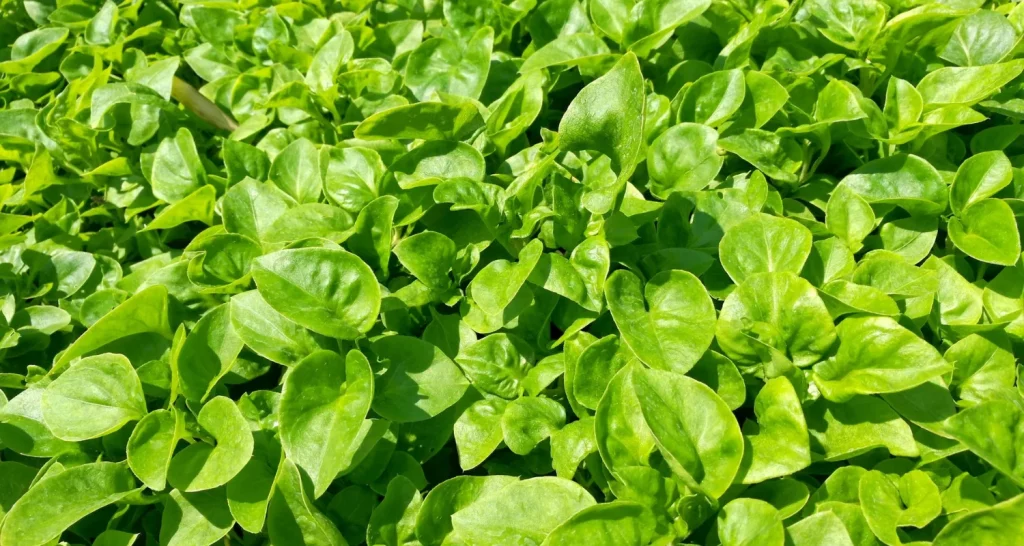

Watercress, commonly used in salads, can be surprisingly effective in treating gum infections. There are three ways to use it to relieve this condition:
- As an extract for mouthwash or gargling.}
- In the form of an infusion.
- Chewing the fresh leaves.
Ingredients
- Watercress, blackberry, St. William’s Wort and lesser burnet.
- Half a liter of water.
Instructions
- Combine approximately 5 g of each herb with water and boil for two minutes. Strain the mixture through cheesecloth.
- Use this liquid as a mouthwash three times a day.
Preventing Gum Disease
Gum disease is treatable, especially in the early stages. Professional cleaning is essential, where plaque and tartar are removed. In more advanced cases, periodontal surgery may be required.
To prevent gum disease, it is essential to:
1. Oral Hygiene :
- Brushing: It is essential to brush your teeth at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing: Flossing should be used daily to remove food debris and plaque from between teeth and under the gum line.
- Mouthwash: May help reduce plaque and bacteria.
- Regular Dental Visits: Visit the dentist at least twice a year for checkups and professional cleanings.
2. Balanced Diet: Diet plays a fundamental role. Eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals and limit the consumption of sugars and fermentable carbohydrates. Excessive consumption of sugars and acidic foods can promote the appearance of bacterial plaque. On the other hand, a diet rich in vitamin C, calcium, antioxidants and omega-3 can strengthen the gums and help prevent periodontal disease.
3. Avoid Tobacco: Smoking is a significant risk factor for the development of periodontitis.
4. Beware of Hormonal Changes: Women, especially during pregnancy, menstruation or menopause, should be aware of increased sensitivity in the gums and take preventive measures.

Education and Prevention:
Oral health education from an early age is essential. Schools and communities are implementing educational programs to teach children the importance of oral hygiene. In addition, awareness campaigns in mass media seek to reinforce the importance of regular dental visits and good habits in adults.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a serious but preventable oral health problem. By adhering to good oral hygiene practices and seeking regular dental care, it is possible to maintain healthy gums and prevent complications associated with this disease. It is essential to act quickly at the first symptoms and follow the dentist’s recommendations to ensure optimal oral health.
Gum disease is a condition that affects millions around the world. With proper information, prevention, and oral care, we can protect ourselves and our loved ones. Don’t forget to visit your dentist regularly and follow an oral hygiene routine to maintain a healthy, radiant smile.
Contact us
If you are experiencing any of these problems and need further guidance, please do not hesitate to visit Channel Island Family Dental .
At Channel Island Family Dental , we will focus on providing you with a timely diagnosis. Additionally, at Oxnard Dentist , Ventura Dentist , Port Hueneme Dentist , and Santa Paula Dentist , they will be able to provide you with the best treatment that will give you back the confidence to smile again.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Literature
- World Health Organization. (2020). Oral health and well-being. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/oral-health
- National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, NIH (Mar, 2023). Periodontal (Gum) Disease. National Institute of Health. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/gum-disease
- Better Health Channel. (May, 2022). Gum Disease.Department of Health, State Government of Victoria, Australia. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/gum-disease
- International Dental Association. (2019). Relationship between periodontal disease and systemic health. Retrieved from https://www.fdiworlddental.org/
- Johns Hopkins MedicineHealth. Periodontal Diseases (n.d.). The Johns Hopkins University, The Johns Hopkins Hospital, and Johns Hopkins Health System. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/periodontal-diseases
- Journal of Clinical Periodontology. (2018). Advances in the diagnosis of periodontal diseases. Retrieved from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/1600051x
- Spanish Nutrition Society. (2021). Nutrition and oral health. Retrieved from https://www.sennutricion.org/
- European Dental Foundation. (2019). Oral health education and prevention. Retrieved from https://www.eudental.eu/
- National Institute of Dental Research. (2020). Symptoms and treatment of gum disease. Retrieved from https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/
- Cleveland Clinic medical. (Oct 04, 2023). Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease). https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21482-gum-periodontal-disease
- National Health Service, NHS report (May, 2023). Gum disease. https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/mouth/gum-disease
- Evan Frisbee, DMD. (July 30, 2021). WebMD, LLC. Gingivitis and Periodontal Disease. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/gingivitis-periodontal-disease