Last Updated on: 4th December 2024, 04:14 pm
Tooth extraction can occur at any time in life. The difference is the procedure. It takes place, according to the life stage. The question is how to pull out a tooth safely. How to handle the change of milk teeth? Can you extract an adult tooth at home? What are the effects of losing a permanent tooth? These are some of the answers you find here.
Around 6 or 7 years of age, the change of milk teeth for the permanent or secondary ones begins. It is a stage of the growth process that generates different emotional conditions in children that understanding parents must handle.
Baby teeth fall out without help. The Mayo Clinic recommends letting them fall out on their own. They should not be removed before the right moment, as they guide the adult teeth and help in jaw development.
However, the extraction of a tooth is not typical of childhood, since in adulthood, it is possible to face dental problems that lead to an extraction procedure, but with a very different kind of management.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow to Extract Milk Teeth?
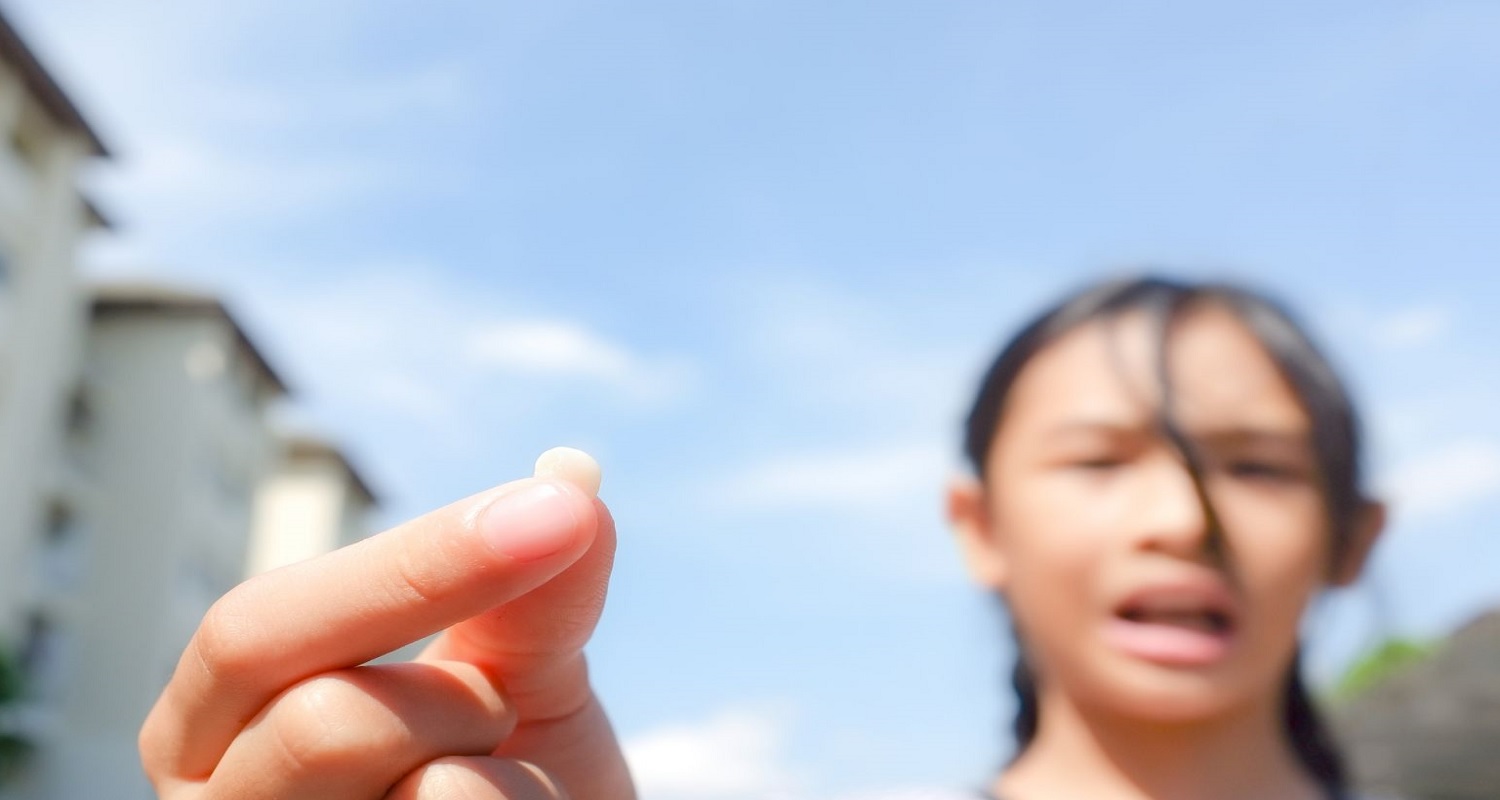

Generally, the first teeth to loosen are the central incisors. The clue to identifying the change is that the tooth moves. A lot of movement is a sign that the piece is ready to go. Moving the tooth with the tongue helps detach it from the gums. Chewing hard or crunchy foods also speeds up tooth eruption. If the tooth is ready to come out, the bleeding will not be excessive.
Here are some fun suggestions that should help reduce the stress of the change process:
- With a length of dental floss, tie one end to a door knob and the other to the loose tooth. By moving the door in the direction that the thread is pulling, the tooth is dislodged and comes out.
- The dog in the house can participate. A portion of dental floss is used. One end is attached to the pet’s collar and the other to the tooth ready to be removed. A provocative treat or morsel is thrown for the dog that will run to reach its prize, and the tooth will come out behind the pet.
- A baseball can be a replacement for a dog. One end of the floss is tied to the ball and the other to the tooth. Then the ball is thrown and a home run is hit: the tooth is out.
Recommendation: As soon as the tooth is removed, it is advisable to bite down on a damp gauze so that the blood clots quickly.
What Milk Teeth are Regularly Extracted?
The first molars and incisor teeth are the most frequently extracted in children. One of the causes that affect primary molars, which have a larger surface area, is the difficulty in reaching them with a toothbrush.
In case of caries in milk teeth, it is pertinent to consult with the dentist to follow the most appropriate procedure.
Although progress has been made in pediatric oral health in recent years, caries and their effect continue to be the cause of milk tooth extraction.
Can you Pull out a Tooth at Home?
It is recommended that this process be performed by a dentist since this is a surgical procedure that requires care to avoid an infection or heavy bleeding.
Permanent teeth have deep roots, nerves, and blood vessels in the jaw, which is why extraction at home can have adverse effects on oral health or leave part of the tooth in the gums, a situation that might cause an infection.
The loss of permanent teeth represents a threat to oral health. Some of the effects are:
- Gingivitis (bleeding or inflammation of the gums)
- Regression of the gums
- Caries in the teeth close to the missing piece
- Infected gums
- Facial effects and bone deterioration
- Difficulty chewing and vocalizing
What should you not do to extract a permanent tooth?
- Biting into an apple pushes the tooth down, damages the gums and bone, or fractures the tooth.
- Moving the tooth with your fingers is a route to infection and damages the dental structure.
- Removing it with dental floss can cause profuse bleeding and intense pain. In addition, it can fracture the tooth and affect nearby teeth.
What Happens When You Lose a Permanent Tooth?
The loss of permanent teeth can be a consequence of cavities, periodontal disease, infections, or root canal treatments with adverse results.
Periodontal disease is a chronic inflammation of the tissues that support the teeth as a result of bacteria. In addition, the entry of these microorganisms into the bloodstream is possible, a situation related to infective endocarditis. Different epidemiological studies show an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in people with active periodontal disease.
In addition, the loss of teeth affects the integral well-being of the person. When the lost tooth is not replaced, the balance of the dental system is altered and various adverse reactions are facilitated, such as the displacement of other teeth and difficulty chewing food, along with its effects on nutrition and vocalization, among others.
A study carried out in 2014 found that people have little information about the consequences of missing teeth, which shows the importance of promoting oral health education in communities.
Post-extraction Care for Adult
In the first 24 hours after the extraction:
- Do not rinse the mouth.
- Consume warm food and drinks, and avoid them through the affected area.
- Avoid drinking alcohol. It does not allow the wound to heal properly and can also cause bleeding.
- Brush the teeth one day after the process, being very careful at the extraction site.
One day after the intervention:
- Rinsing with salt water helps eliminate bacteria. Dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a glass of water and swish the saline solution for 30 seconds in the extraction area. Then spit it out.
- To calm the pain, an analgesic should be taken: acetaminophen, ibuprofen or sodium naproxen. Oral health specialists recommend not taking aspirin for pain management, as this medication can affect coagulation.
- Taking vitamin C will help the recovery process.
Caring for your Teeth
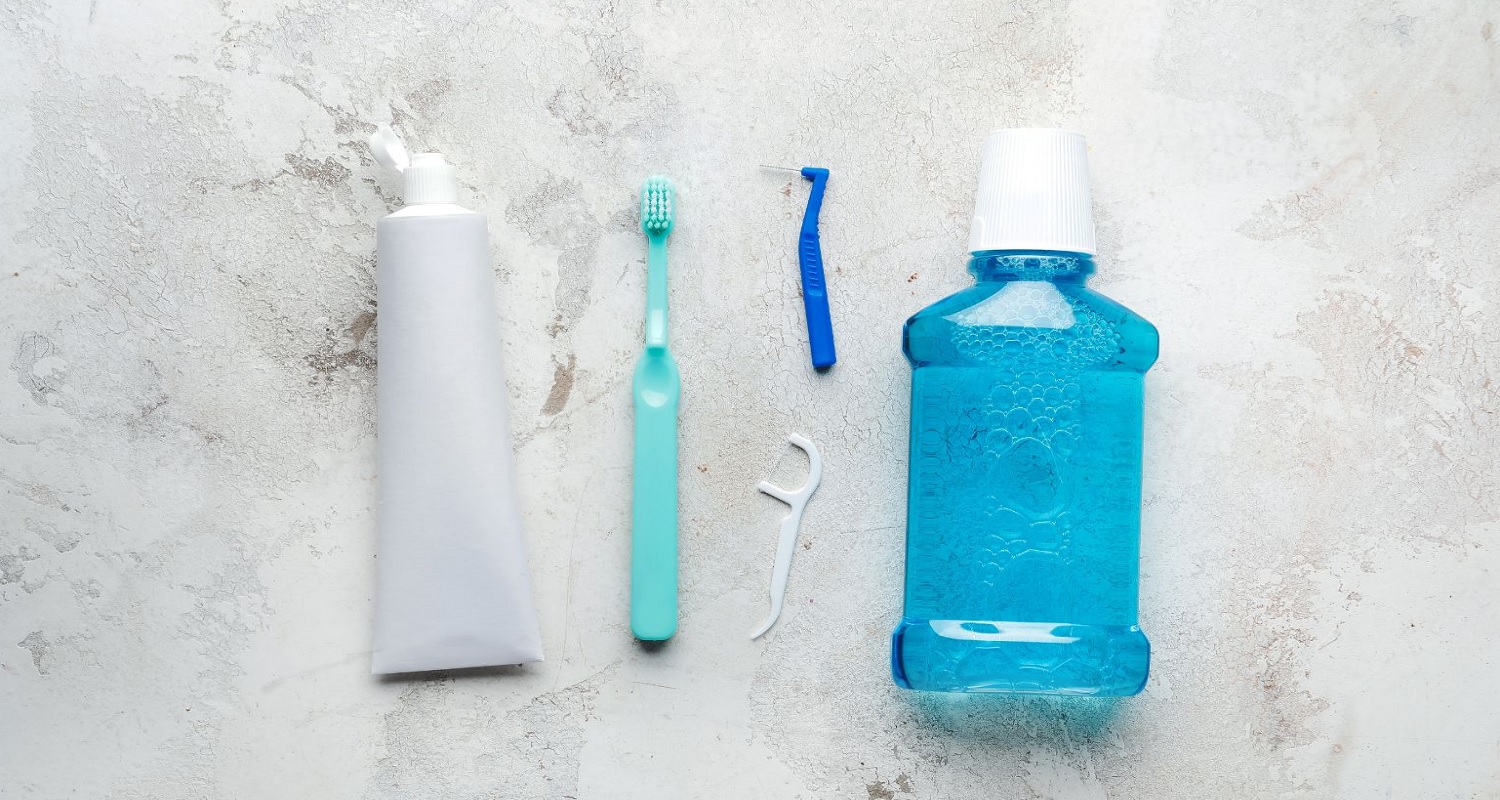

- Daily dental hygiene is the best way to prevent oral health problems.
- Use fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash at least twice a day, or after meals.
- Floss daily to remove food debris in places where the brush does not have good access.
- Visit the dentist at least twice a year for cleaning.
- Limit the consumption of drinks or foods with high levels of sugar, which makes the teeth more vulnerable to decay.
- Avoid smoking, which can cause gum disease and tooth loss.
It is recommended that children be careful to avoid the use of force. Only if the tooth is very loose, is it possible to extract it with other methods. Otherwise, it could affect the emerging permanent tooth or generate a dental problem in the gums. In addition, it may cause acute pain and inflammation.

It is important to bear in mind that the management of pain and discomfort, or dental extraction in this case, is different for adults and children. If you do not feel sure about the extraction of a milk tooth in a child, visit a pediatric dentist for greater safety. In the case of an adult, the attention of a professional, preferably an endodontist, is essential.
Contact us
If you have any questions about this or other topics, you can contact us at Channel Islands Family Dental as well as our page on Facebook. We look forward to your visit and we will make a timely diagnosis. Our dentists in Oxnard, Santa Paula, Ventura, Newbury Park, and Port Hueneme will be able to guide you toward the best treatment to take care of your health and give you back your best smile.
Bibliography
- Alsheneifi, T / Hughes, C (2001). Reasons for dental extractions in children. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4201933/
- Dosumu, O et al (2014). Knowledge of consequences of missing teeth in patients attending a prosthetic clinic in UCH Ibadan. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4201933/
- Jewell, Tim (2018). How Do I Pull Out My Child’s Baby Tooth, and Can I Also Pull My Own? https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-pull-out-a-tooth
- Quesada-Chaves, Daniel (2018). Relationship between periodontal disease and cardiovascular disease. The need for a management protocol. Costa Rican Journal of Cardiology. https://www.scielo.sa.cr/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1409-41422018000400037&lang=es
- Vu, Tu Anh et al (2022). How to pull out a loose tooth. https://www.wikihow.com/Pull-Out-a-Loose-Tooth