Last Updated on: 4th February 2026, 10:48 am
A broken tooth emergency needs fast dental care to reduce pain, prevent infection, and save the tooth. Even small cracks can get worse without treatment. Seeing an emergency dentist as soon as possible helps protect your smile, avoid complications, and restore normal function, especially for children and teens with permanent teeth.
A broken tooth can happen from falls, sports, accidents, or biting hard objects—and it’s more than just a cosmetic issue.
Upper front teeth, especially the central incisors, are most often affected, and dental trauma is common in children and teens, with 1 in 2 experiencing it between ages 8 and 12.
Quick action can prevent pain, infection, and long-term dental problems. If you live near Oxnard, Newbury Park, Ventura, Santa Paula, or Port Hueneme, Channel Islands Family Dental Office is here to provide fast, gentle, and expert care to protect your smile.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow does a broken tooth happen?
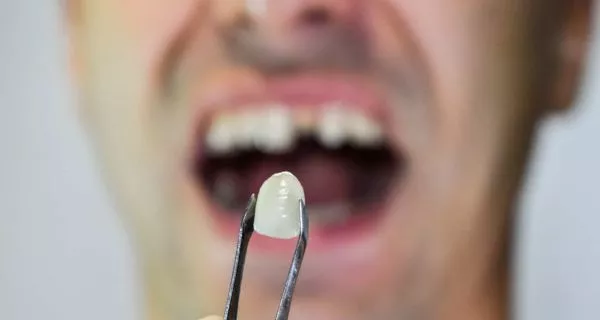
A broken tooth usually happens when the mouth receives a sudden hit or strong pressure. When this happens, the force goes directly to the tooth, and the tooth must absorb that impact. If the pressure is too much, the tooth can crack or break.
Several factors influence how serious the injury is and whether the tooth breaks or not. These factors help dentists understand why a broken tooth emergency happens:
- Strength and direction of the hit: A strong hit or a direct blow to the front of the mouth is more likely to break a tooth than a light or side impact.
- Speed of the impact: Fast accidents, like falls or sports collisions, usually cause more damage than slow pressure.
- Shape and hardness of the object: Hard or sharp objects, such as balls, floors, or metal surfaces, can break a tooth more easily than soft objects.
- Position of the tooth: Teeth that stick out or are in the front of the mouth are more exposed and easier to injure.
When the tooth absorbs most of the impact, it can crack or fracture. In many cases, the gums and bone around the tooth stay healthy. This is important, because it means the tooth often can be treated and saved if care is received quickly.
A broken tooth emergency does not always mean tooth loss, especially with fast professional treatment.
What are the main types of dental fractures in a broken tooth emergency?
Not all broken teeth are the same. The type of fracture depends on how deep the break goes and which part of the tooth is affected. Knowing the difference helps explain why some cases are simple and others need urgent care.
- Crown (coronal) fracture: This fracture affects the visible part of the tooth. It can be:
- Uncomplicated, when only the enamel and dentin are involved.
- Complicated, when the fracture reaches the nerve inside the tooth.
When the nerve is affected, pain is usually stronger and immediate dental care is very important.
- Crown–root fracture: This type of fracture affects both the crown (the visible part of the tooth) and the root below the gum line.
- It may cause pain when biting and can be harder to treat because part of the damage is hidden under the gums.
- A careful dental exam and X-rays are needed.
- Root Fracture: The break happens only in the root of the tooth, below the gums.
- It is not always easy to see, but it can cause pain, tooth movement, or discomfort when chewing.
- Treatment depends on the location of the fracture and how stable the tooth is.
In any of these cases, acting fast during a broken tooth emergency helps protect the tooth and avoid complications. The caring team at Channel Islands Family Dental Office is here to help families in Oxnard, Ventura, Santa Paula, Port Hueneme, and Newbury Park with gentle and timely dental care.
What to do immediately after a broken tooth?

If your tooth breaks, acting quickly can make the difference between saving it or losing it. Follow these steps while heading to your dentist:
- Stay calm and assess the situation: Check for pain, bleeding, or loose pieces of the tooth. Avoid moving the tooth forcefully.
- Rinse your mouth with lukewarm water: This cleans the area and lowers the risk of infection. Avoid alcohol or strong mouthwashes that may irritate.
- Control any bleeding: Gently press a clean gauze on the gum for 10–15 minutes to stop bleeding.
- Save any tooth fragments: Place broken pieces in a cup of milk or saliva. Your dentist may be able to reattach them.
- Relieve pain temporarily: Take an age-appropriate pain reliever if needed. Apply a cold compress to the cheek to reduce swelling.
- Avoid chewing on the broken tooth: Stick to soft foods and keep pressure off the affected tooth until you receive professional care.
- See a dentist immediately: Contact a local emergency dentist, like Channel Islands Family Dental Office in Oxnard, Ventura, Santa Paula, Port Hueneme, or Newbury Park. Prompt care increases the chance of saving the tooth.
What are the main risk factors for a broken tooth emergency?
A broken tooth emergency can happen to anyone, but some situations increase the risk. These include:
- Contact or high-impact sports
- Car accidents or falls
- Biting hard objects like ice or hard candy
- Children with physical or developmental disabilities
- Cleft lip or palate
- Weak enamel (like Amelogenesis Imperfecta)
- Limited access to regular preventive dental care
Knowing these risks helps families stay alert and seek early care.
How is a broken tooth emergency diagnosed?
A broken tooth emergency needs a fast and careful diagnosis. The goal is to understand how serious the injury is and choose the best treatment to protect the tooth. Dentists usually follow three simple steps to evaluate the problem.
What questions are asked during dental history (anamnesis)?
The first step is talking with the patient or the parents in a calm and reassuring way. The dentist will ask questions to understand what happened and how much time has passed since the injury, such as:
- When did the injury happen?
- How did it happen?
- Is there pain, bleeding, or tooth movement?
These answers help the dentist decide how urgent the broken tooth emergency is and what care is needed next.
What happens during the clinical examination?
Next, the dentist carefully examines the mouth to look for visible signs of injury. This includes checking both the soft and hard tissues.
The dentist will look at:
- Soft tissues, such as the gums, lips, cheeks, and tongue, to find cuts or swelling.
- Hard tissues, including the teeth and jawbone, to identify fractures or damage
Other checks may include:
- Tooth mobility
- Size of the fracture
- Sensitivity to hot or cold
This step helps confirm how much of the tooth is affected.
Why are dental x-rays important in a broken tooth emergency?

Some damage cannot be seen with the eyes alone. Dental X-rays allow the dentist to see inside the tooth and below the gums.
In a broken tooth emergency, dental trauma guidelines often recommend:
- Occlusal X-rays
- Three periapical X-rays taken from different angles
These images give a clear view of the tooth, root, and surrounding bone, helping the dentist make an accurate diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for a broken tooth emergency?
Treatment depends on how deep the fracture is and whether the nerve, root, or bone is involved. The main goal is to save the tooth, relieve pain, and restore normal function.
Early treatment is very important for long-term results. The success of care depends on the size and depth of the fracture, any damage to the gums or bone, the stage of root development, and the type of treatment needed. Acting quickly also helps reduce pain, protect appearance, and provide emotional comfort, especially for children.
How are uncomplicated tooth fractures treated?
When the nerve is not affected, treatment is usually simple and effective:
- Enamel only: a basic restoration and routine follow-up
- Enamel and dentin: pulp protection, restoration, and regular dental control
With early care, these fractures often heal well and keep the tooth strong.
How are complicated tooth fractures treated?
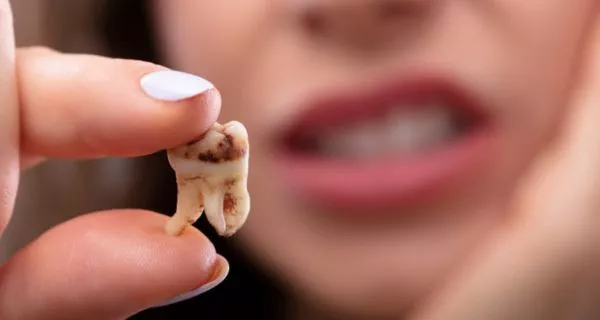
When the fracture reaches the nerve or deeper parts of the tooth, more advanced care is needed:
- Pulp exposure (crown only): Root canal treatment and a crown or inlay restore the tooth.
- Crown–root fracture: Affects both the visible part and the root; may need stabilization or minor surgery.
- Root Fracture: Happens below the gums; treatment depends on stability and may include root canal therapy.
- Tooth and bone fracture: Severe cases often require hospital care, and the dentist may need to reposition the tooth if it has shifted.
The goal of treatment is always to save the tooth whenever possible. Early care, proper restoration, and stabilization increase success.
However, in the most severe cases—such as extensive crown–root or tooth-and-bone fractures—it may not be possible to save the tooth, and extraction becomes the last option.
Where can you get help for a broken tooth emergency near you?
Dental emergencies can happen at any time, and you never know when a tooth might break. That’s why our team at Channel Islands Family Dental Office is always ready to help.
We proudly serve families in Oxnard, Newbury Park, Ventura, Santa Paula, and Port Hueneme. Our friendly, expert dentists are here to guide you, provide emergency care, and offer the best treatment options to protect your smile.
Don’t wait—call today and schedule your visit. Early care can make all the difference in saving your tooth and reducing pain.
FAQs
Voice and Search Snippets (Q&A)
References
1. DiAngelis, A. J., Andreasen, J. O., Ebeleseder, K. A., Kenny, D. J., Trope, M., Sigurdsson, A., Andersson, L., Bourguignon, C., Flores, M. T., Hicks, M. L., Lenzi, A. R., Malmgren, B., Moule, A. J., Pohl, Y., & Tsukiboshi, M. (2012). International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth. Dental Traumatology, 28(1), 2–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-9657.2011.01103.x
2. Li, F., Diao, Y., Wang, J., Hou, X., Qiao, S., Kong, J., Sun, Y., Lee, E., & Jiang, H. B. (2021). Review of Cracked Tooth Syndrome: Etiology, Diagnosis, management, and Prevention. Pain Research and Management, 2021, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3788660
3. Patel, J. (2022). Dental Trauma: A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and management. Dental Traumatology, 38(3), 250–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/edt.12747
4. Watson, S. (2025, November 18). How to care for a cracked or broken tooth. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/toothache-relief-from-a-cracked-or-broken-tooth-1059317
5. WebMD. (2024, October 14). Handling dental emergencies. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/handling-dental-emergencies