Last Updated on: 21st May 2024, 09:02 am
Saliva performs a fundamental function in oral health, such as lubricating the oral mucosa and teeth, maintaining the balance of oral microorganisms, regulating the pH of the mouth, and facilitating swallowing. But what happens when these functions are altered? Certain diseases such as xerostomia can occur with harmful consequences for oral health. Xerostomia, or dry mouth, occurs when there is low production of saliva and may be a side effect of some medication or an imbalance in overall health.
What Are The Causes of Dry Mouth?
The alteration in the functioning of the salivary glands can have various causes; the most frequent are:
-
- Medications: Antidepressants, anti-inflammatories, and antihistamines can cause dry mouth as a side effect.
- Aging: Age is a factor that determines the amount of decreased saliva production.
- Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy: Patients suffer from xerostomia as a result of these cancer treatments.
- Tobacco and Alcohol: Tobacco and alcohol use decrease normal salivation.
- Recreational drug use: The consumption of methamphetamine can cause severe dry mouth
- Autoimmune diseases: Among them are Sjögren’s syndrome, lupus erythematosus, and HIV.
- Systemic diseases: Diabetes and some psychiatric diseases such as depression or anxiety.
Symptoms of dry mouth
The main symptom is dryness, but there are also other common signs and symptoms such as:
-
- Thick, viscous saliva.
- Alteration of the taste of food.
- Problems chewing, speaking, and swallowing.
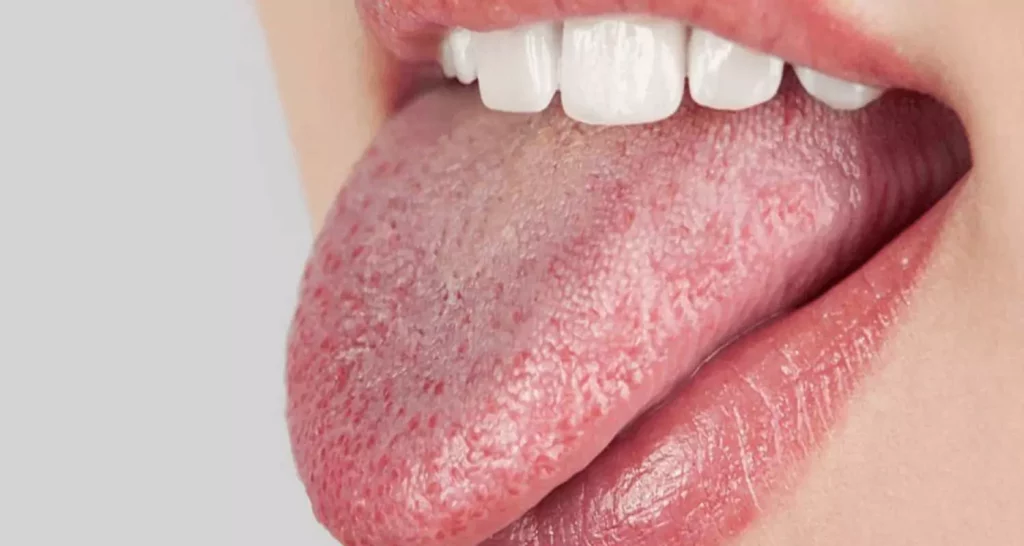
- A cracked tongue that produces a burning sensation
- Cracks at the corner of the lips (angular cheilitis)
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Dry and flaking lips.
Dry Mouth Treatments
The treatment of dry mouth should be directed mainly at the cause. After that, many alternatives can be considered, including:
-
- General preventive measures such as drinking plenty of water to improve hydration. Avoid alcohol and tobacco consumption, as well as coffee, and reinforce good oral hygiene techniques.
- Medications: Certain medications help stimulate the salivary glands, among them pilocarpine, anetolditiolthione, and bromhexine. These drugs should be administered only under a doctor’s supervision.
- Salivary stimulants: chewing is an effective stimulus to increase saliva production, therefore chewing gum is recommended.
- Salivary substitutes: These are used when there is no response to the needed salivary stimulation. They act as lubricants for the oral mucosa and while they are composed of cellulose and water, their effect is of limited duration and requires frequent use.
Natural remedies for dry mouth
-
- In addition to the appropriate treatment, in cases of mild xerostomia, the medical professional treating the patient could authorize the use of some natural remedies that can help combat the discomfort derived from xerostomia, such as:
- Ginger: Because it has a spicy taste, it is considered useful to stimulate salivation. It can be consumed with lemon water; however, it is not recommended if there are cracks or wounds on the tongue and the corners of the lips.
- Aloe vera: a natural painkiller that can relieve the burning sensation in the mouth. It can be used as a mouthwash.
- Chamomile with mint: An infusion of chamomile with mint could also help stimulate saliva production. In addition, mint provides analgesic properties and is very effective against bad breath.
Dry mouth and medical conditions
Some systemic disorders are less likely to cause dry mouth syndrome, but it is common in Sjögren’s syndrome and can also occur in an HIV infection, uncontrolled diabetes, and neurological disorders such as depression.
-
- Diabetes and systemic diseases: diabetics tend to become dehydrated by frequently eliminating excess urine; this exacerbates a dry mouth. In addition, other diseases also favor dehydration, resulting in little saliva production.
- Autoimmune diseases: In diseases such as HIV, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome, or lupus erythematosus, the proper functioning of the salivary glands is altered.
- Anxiety and depression: Stress anxiety causes the contraction of the blood vessels, making it difficult to irrigate the salivary glands, which is why they do not produce an adequate amount.
Dry mouth and cancer treatment
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can produce alterations in the salivary glands and aggravate the discomfort of the cancer patient, making him or her prone to other oral conditions.
-
- Radiotherapy: Ionizing radiation administered to the head and neck area, as a common cancer treatment, can negatively and even seriously affect the salivary glands and therefore affect salivary flow. In fact, it can be decreased by up to 50%. In such cases, recovery can take 6 to 12 months.
- Chemotherapy: saliva may present changes in its composition or slightly decrease the amount. In general, these alterations are transient and less severe than those produced by radiotherapy.
Dry Mouth and Oral Health
The decrease in saliva interferes with the protection against bacteria since saliva acts as a protective barrier against microorganisms, which makes the mouth more vulnerable to various oral problems:
-
- Bad breath
- Wounds in the mouth, tongue, and lips.
- Gingival and periodontal disease
- Increased incidence of dental caries
- Problems eating and speaking.
- Change in taste.
- Problems placing a prosthesis due to a lack of lubrication.

Remember that the dentist is the right person to advise you on the habits you must maintain, so do not hesitate to visit your dentist’s office frequently.
Contact us
If you have any questions about oral conditions that cause dry mouth or other topics, you can contact us at Channel Islands Family Dental as well as our page on Facebook. We look forward to your visit and we will make a timely diagnosis. Our dentists in Oxnard, Santa Paula, Ventura, Newbury Park, and Port Hueneme will be able to guide you toward the best treatment to take care of your health and give you back your best smile.
Bibliography
- Cancer.Net Editorial Board (2016) Dry Mouth or Xerostomia. https://www.cancer.net/es/asimilaci%C3%B3n-con-cancer/efectos-fisicos-emocionales-y-sociales-del-cancer/manejo-de-los-efectos-secundarios-fisicos/sequedad-en-la-boca-o-xerostomia
- Dental and Craniofacial Research Institute (2019) Dry mouth. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/espanol/temas-de-salud/la-boca-seca
- Blanco, A. (2014) Oral pathology associated with dry mouth. https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0213-12852014000300005
- De La Paz, T. (2014) Dry mouth: causes, diagnosis, and treatment. https://revzoilomarinello.sld.cu/index.php/zmv/article/view/153/273
- Medical News Today (2019) Everything you need to know about dry mouth. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/187640#_noHeaderPrefixedContent
- Coimbra, F. (2009) Xerostomia. Etiology and Treatment. Rev.Portuguesa de Estom. Med. Dental and Cir. Maxilofac.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1646289009701177