Last Updated on: 4th December 2024, 05:23 pm
Whenever we talk about a toothache, we associate it with factors such as gum disease (periodontitis), cavities, and injuries. Early warning signs of mouth cancer will always be on the end of the list. However, sometimes, we present symptoms associated with diseases we do not know we suffer from or simply did not know could present pain or discomfort in the teeth. Another factor that can generate such symptoms is side effects derived from pharmacological treatments used to manage a health condition.
Upon experiencing toothache symptoms, we should attend a dental review to see if the dentist suspects a toothache is associated with a tumor. Sometimes, a toothache is routine, but if it increases over time when brushing the teeth, we should check it out. Hopefully, we will find no apparent lesions that indicate an obvious dental problem.
This is why it is important not to let facial pain go by, and even more so when it is located mainly in the jaw, it is suggested to have a check-up when the pain is persistent to see if a serious condition is presenting.
Early warning signs of mouth cancer
People have no idea how common is oral cancer and that it can develop throughout the mouth but is commonly seen in the lips, gums, and sometimes the throat.

The most common symptoms of mouth cancer are:
- Painful mouth sores that do not heal within several weeks
- Persistent, unexplained lumps in the mouth that do not go away
- Persistent, unexplained lumps in the lymph nodes in the neck that do not go away
Other symptoms that may occur include:
- Pain or difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Changes in your voice or speech problems
- Unintentional weight loss
- Bleeding or numbness in the mouth
- One or more loose teeth for no apparent reason or a tooth socket that does not heal after a tooth is removed (extraction)
- Difficulty moving the jaw
- Red or white spots on the lining of the mouth. These are common and are rarely a sign of cancer, but sometimes they can develop into cancer, so it is worth consulting a doctor if you have them.
Among the most descriptive symptoms or associated with early warning signs of mouth cancer in the mouth we have:
Jaw pain
Mainly this symptom is associated with the growth of metastatic tumors (cancer formed in another part of the body that spreads, affecting other organs) in the oral cavity. The pain decreases the ability to chew, speak, and eat properly. Sometimes this pain is associated with injuries to the jaw and sometimes it can be related to oral cancer. When you have jaw pain and it worsens over time, you may experience facial pain that manifests other symptoms such as muscle tenderness, swelling of the face, earaches, or clicking noises when you open or close your mouth.
Lumps in the jaw
Some people only have one symptom of jaw cancer. These lumps may be indicators that cancer is forming in the jaw under the tissue. If you notice new lumps in your mouth that have not gone away after two weeks, it is important to contact a dentist. Other times, it is possible that lumps appear on the palate or near the gums; In case this happens to you, contact a dentist as soon as possible.
Swollen jaw
Osteosarcoma is a type of cancer that develops in immature bone; its main symptom is swelling of the jaw. This tumor affects the jaw and may be malignant. Swelling is usually localized on one side of the face, but on some occasions, it can also develop inside the mouth. Swelling may be bound on the face, upper palate, or gums, depending upon the location of the tumor.
Causes of Oral Cancer
Currently, doctors and scientists have not been able to determine with certainty the causes of oropharyngeal and oral cavity cancer. However, it is associated with certain risk factors that have the ability to modify cells, turning them into cancerous ones.

When cancerous cells appear, it is usually due to the modification or expression of these genes found in DNA. DNA is the chemical in our cells that makes up our genes (the instructions for how our cells work). These genes are responsible for looking like our parents and they can affect more than just appearance. Some genes called proto-oncogenes help control when cells grow and divide; sometimes changes in DNA can cause these genes to promote cell division, calling them oncogenes. Therefore, cancer can be caused by changes in DNA, creating oncogenes and turning off the genes that suppress tumor growth.
RISK FACTORS
Factors that can increase the risk of mouth cancer include:
- The use of tobacco, including cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco and snuff, among others
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages
- Excessive sun exposure to the lips
- Ultraviolet (UV) light
- Deficient nutrition
- Genetic syndromes (inherited defects (mutations) as some genes imply a very high risk of developing mouth and throat cancer)
- A sexually transmitted virus called human papillomavirus (HPV)
- A weakened immune system
- In Southeast Asia, South Asia, and other parts of the world, it is common to chew betel quid, made from a mixture of areca nut (betel nut), spices, lime, and other ingredients. Many people in these areas also chew gutka, a mixture of betel quid and tobacco. The risk of mouth cancer is higher in people who chew betel quid or gutka.
What is the difference between mouth ulcer and oral cancer?
At any time in life, everyone has experienced oral ulcers, which are painful and always located in moist areas such as the cheeks, tongue, gums, or palate. They are commonly known as “oral canker sores”, however, their technical name is “aphthous ulcers” and there is no specific cause for their origin, but they usually heal easily and do not last more than two weeks.
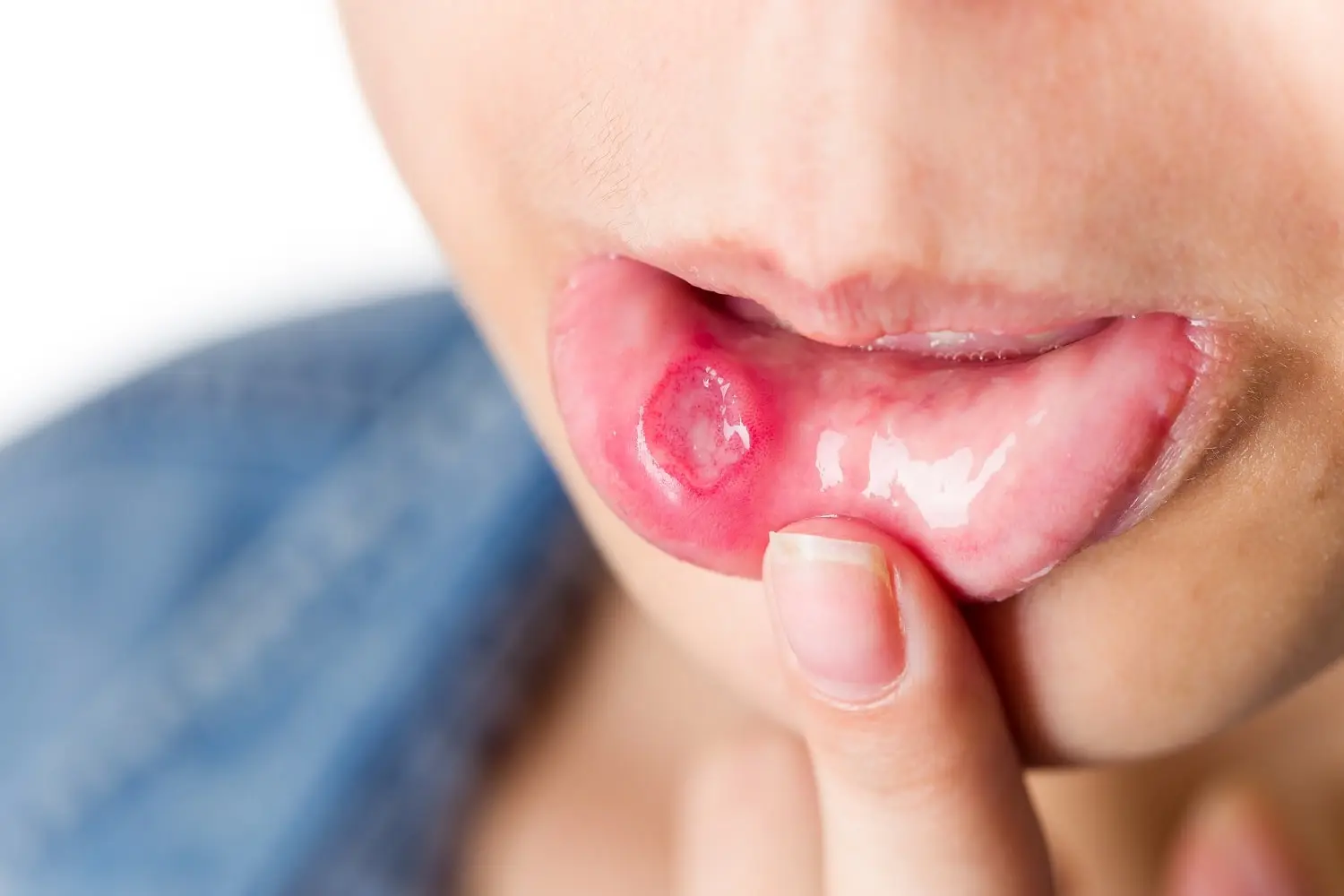
Canker sores differ from candidiasis or vitamin B deficiency, because for these conditions they may manifest as very painful, sometimes large and irregular cracks. There can also be canker sores that can be painful and others that are not, generated by different diseases (Lupus, Chickenpox, HIV, Crohn’s disease, Herpes, etc.) and can spread throughout the mouth.
So how could we differentiate the characteristics of canker sores from cancer? These and other symptoms are explained below:
- A mouth ulcer that does not heal (this is the most common symptom).
- Mouth pain that persists (also very common).
- A lump or thickening in the cheek
- White or red sores on the gums, tongue, tonsils, or lining of the mouth — may bleed
- A sore throat or the feeling that something is stuck in the throat that does not go away
- A white or yellow film, patches or pus in the mouth or on the tongue
- Swelling of the gums, mouth, or throat
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing, the sensation of dryness, and pain.
- Difficulty moving the jaw or tongue
- Numbness of the tongue or other area of the mouth
- Loosening of the teeth or pain around the teeth or in the jaw
- Voice changes
- A lump or mass in the neck
- Weight loss
- Constant bad breath
It should be noted that patients who have already been diagnosed with some type of cancer and receive mouth cancer treatment easily develop mouth ulcers.
In conclusion, we must be attentive to any changes observed in our mouths. Nothing should be overlooked, so schedule regular visits with the dentist; and in case of presenting any symptoms or signs, report it in a timely manner so they can do a proper diagnosis and start treatment. Always seek advice from an expert and avoid home management in the face of risk factors.
Contact us
If you have any questions about this or other topics, you can contact us at Channel Island Family Dental and on our Facebook page. We look forward to your visit and we will make a timely diagnosis. Our dentists in Oxnard, Saint Paula, Ventura, Newbury Park, and Port Hueneme will be able to guide you towards the best treatment to take care of your health and give you back your best smile.
Bibliography
- American Cancer Society. About Oral Cavity and Oropharyngeal Cancer. Cancer Information, Answers, and Hope (Internet). consulted on Sep 14, 2022. Available on: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/oral-cavity-and-oropharyngeal-cancer/about.html
- Mayo Clinic Staff. Mouth cancer. Mayo Clinic (Internet). Review on October 20, 2020 (consulted on September 14, 2022). Available on: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/mouth-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20350997
- Mouth cancer. NHS. Review on Oct. 14, 2019 (consulted on Sep 14, 2022). Available on: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/mouth-cancer/symptoms/
- The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (internet). Canker sore vs. oral cancer: How can you tell the difference? Published on Sep 14, 2022; (consulted on Sep 26, 2022). Available on: https://www.mdanderson.org/cancerwise/canker-sore-vs–oral-cancer–how-can-you-tell-the-difference.h00-159542901.html