Last Updated on: 19th December 2025, 06:38 am
What is a Dental Abscess and How Does it Affect our Oral Health?
A dental abscess is a condition that, despite being commonly seen in dental offices, may be unknown to many. This article aims to explain what a dental abscess is, identify its symptoms, the causes and risks it entails, and above all, ways to treat and prevent it to maintain optimal oral health.
What is a Dental Abscess
When we talk about a dental abscess, we are referring to a condition that not only causes significant pain and discomfort but can also be an indication of a more serious oral health problem.
A dental abscess is a collection of pus that develops in the teeth or gums due to a bacterial infection. This pocket of pus can cause severe pain and other worrying symptoms. Its presence in the mouth may signal a major underlying problem that requires immediate medical attention.
Types of Abscess
It typically occurs in two forms: periapical, when it affects the tip of the tooth root, and periodontal, which involves the supporting tissue of the teeth, such as the gums. ach is related to different structures in the mouth.
1. A periapical abscess originates on the inside of the tooth and can extend to the bone.
2. A periodontal abscess, on the other hand, is formed in the supporting tissues of the teeth.
Although different in location and treatment, both require professional dental care to prevent the spread of the infection and other serious complications.
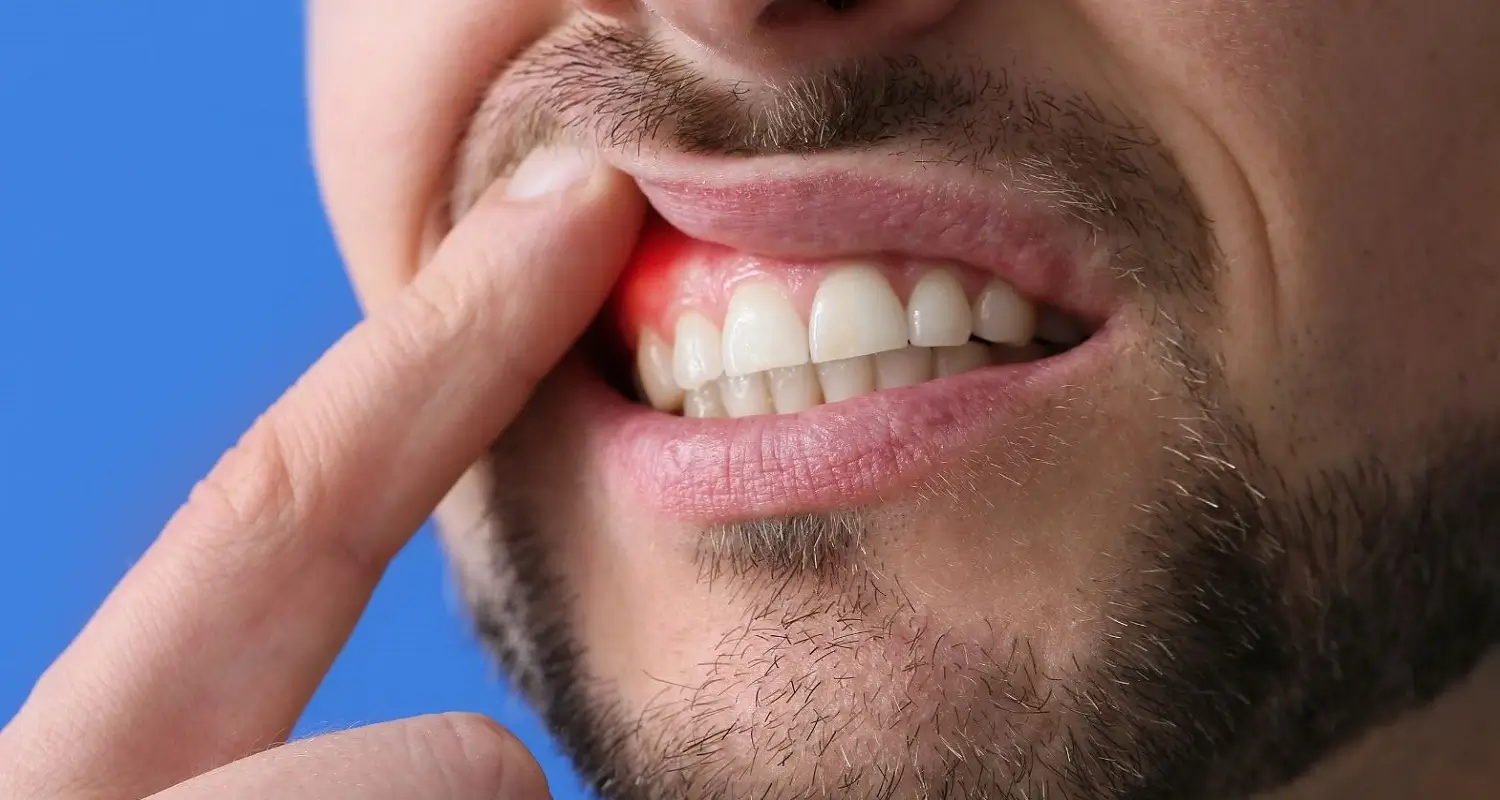
Symptoms and Signs of Tooth Abscess
Identifying a dental abscess is vital to seeking treatment promptly. Common symptoms include severe, stabbing pain in the affected tooth, which may radiate to the ear, jaw, or neck. Sensitivity when chewing or touching the tooth, as well as extreme sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, are also indicative.
Additionally, swelling of the face or gum over the infected tooth may occur, and in some cases, fever or an unpleasant taste in the mouth. These signs should be enough to seek medical and dental assistance.
It is not uncommon for patients not to be able to identify these symptoms immediately, attributing them to less serious dental problems. However, if severe pain accompanied by swelling and signs of infection is experienced, it is crucial to seek dental care.
Risk Factors and Causes of Dental Abscess
Various factors contribute to the formation of a dental abscess. Knowing them is crucial to take the necessary measures and to avoid major complications.
Factors that increase the risk
Untreated cavities, dental trauma, periodontal disease, and poor oral hygiene are the main risk factors for developing a dental abscess, as they allow plaque to accumulate and cause cavities and gum disease.
Diets rich in sugars and carbohydrates, as well as smoking and alcohol consumption, also increase the risk.
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with certain medical conditions or who are being treated with immunosuppressive medications may be more susceptible to infections, including those that lead to dental abscesses.
Main causes of tooth abscess
The causes include untreated dental caries, cracks in the teeth that allow bacteria to enter, periodontitis, and the presence of foreign bodies in the gums. Each of these causes has its treatment approach to prevent abscess development.
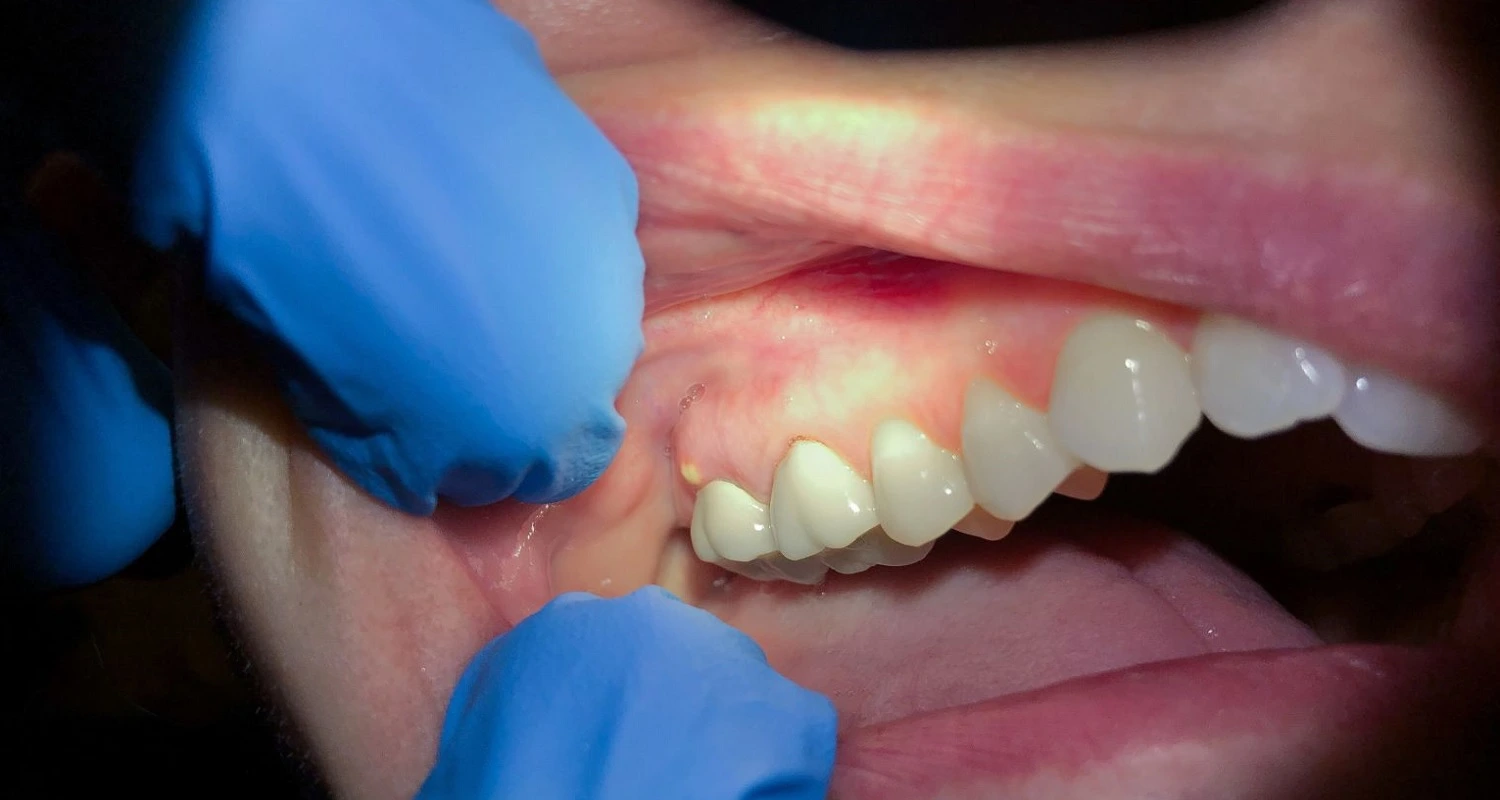 Current Treatments for Tooth Abscess
Current Treatments for Tooth Abscess
The treatment of a dental abscess aims to eliminate the infection and prevent future complications.
Proper care of a dental abscess is crucial to preventing it from becoming a serious problem that puts overall health at risk.
1. Treatment options available
Antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the infection, although their use will depend upon its severity and spread. In addition to medications, specific dental procedures, such as abscess drainage, are essential. In the case of periapical abscesses, a root canal treatment may be necessary to remove the affected part of the tooth and save it.
If the infection is particularly severe or the tooth cannot be saved, tooth extraction may be the best option. It is important to understand that antibiotics alone do not cure an abscess; drainage is essential. In some cases – especially if the infection has spread significantly – oral surgery or emergency treatment may be required.
Therefore, a tooth abscess may include the administration of antibiotics, drainage of pus, root canals, tooth extractions, and in severe cases, hospitalization. Treatment will depend upon the severity of the abscess and the patient’s general health.
2. Steps to follow in treatment
The treatment process begins with identifying the cause of the abscess, followed by administering medications for the infection and pain relief. Subsequently, we proceed with drainage and correction of the source of the infection, such as root canal treatment or extraction of the affected tooth.
3. Innovative treatments
Emerging treatments include the use of lasers for abscess drainage and tissue regeneration, as well as the development of new filling materials that fight bacteria. These innovations seek to not only treat but also prevent future dental problems.
Home Care
As already indicated, some treatments can be performed in a dental consultation. However, sometimes this is not immediately possible, so here are some alternatives:
- To relieve inflammation and facial and jaw pain, apply ice or a cold compress to the outer cheek for 10 to 20 minutes each time. Use a thin cloth to separate the ice from the skin.
- It is important to follow the instructions for taking antibiotics. Do not stop using them just because you feel better. Complete the entire treatment cycle.
- During the first few days, it is advisable to consume liquids, preferably cold.
- Perform mouth rinses with a saline solution and be careful when brushing after the intervention in the first hours.
- Start eating soft foods and maintain rigorous dental hygiene to avoid food residue in the mouth.
- In situations where there is direct contact with food and an open wound, dental hygiene is crucial. Attend regular dental check-ups to monitor the condition’s progression. A common practice is to rinse the mouth several times a day with salt water, which can help control the infection by eliminating bacteria.
- Clove oil is another home remedy suggested for treating oral infections. A little of this oil can relieve pain due to its anesthetic and antibacterial properties, which help fight the abscess. Explore the top 15 natural antibiotics in our article and safeguard your dental health naturally.
- Baking Soda Paste: The pH Balancer: Baking soda fights infections and reduces acidity in your mouth. Make a paste with baking soda and water, apply it to the affected area, and rinse after a few minutes. It’s like a mini detox for your tooth!
- Garlic: The Natural Antibiotic Warrior: Not just a kitchen staple, garlic is a powerhouse against infections. It contains allicin, which fights bacteria. Crush a garlic clove, apply it to the affected area, and let the natural antibiotic do its work.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Rinse: The Bacteria Buster: Dilute hydrogen peroxide with equal parts water. Swish the solution in your mouth and spit it out. This potent ally battles bacteria and relieves discomfort.
- Peppermint Tea Bags: The Cooling Comforter: Used tea bags, especially peppermint, can soothe your abscess. Cool a used tea bag and gently hold it against the tooth. Peppermint’s natural properties work to calm the storm in your mouth.
Additionally, pain can be treated with over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen. Be cautious when using medications. It is crucial to read and follow all the instructions on the product label. If your doctor has prescribed a painkiller, use it as directed. If you are not taking a prescribed painkiller, consult your doctor about the possibility of using an over-the-counter one.
Tooth Abscess Prevention
Prevention is key in the management of a dental abscess. Maintaining proper oral hygiene and regular visits to the dentist help to avoid the appearance of abscesses.
Importance of oral hygiene
Proper oral hygiene is the first line of defense against tooth abscesses. This includes regular brushing, flossing, and mouthwash, as well as professional teeth cleaning. It is also important to limit the intake of sugary foods and drinks that contribute to the formation of cavities, one of the main causes of abscesses.
Tips to Prevent Dental Abscesses

1. Brush your teeth twice a day and floss daily.
2. Limit the intake of sugars and acids that can damage tooth enamel.
3. Wear mouthguards during sports activities to avoid trauma.
4. Schedule regular visits to the dentist for checkups and professional cleanings.
These visits not only provide professional cleanings but also allow the dentist to detect and treat problems such as cavities and periodontal disease before they become abscesses. The use of fluoride mouthwashes and the application of dental sealants are other recommended preventive measures.
Complications Derived from a Dental Abscess
If not treated properly, a tooth abscess can have serious and life-threatening consequences.
Common complications
Complications include the spread of the infection to other parts of the body, loss of the affected tooth, jaw bone problems, and, in extreme cases, sepsis. These complications underline the importance of treating a dental abscess in time.
Warning signs to seek medical attention
Warning signs include increased pain, difficulty breathing or swallowing, high fever, and excessive swelling of the face or neck. Faced with these symptoms, immediate medical attention should be sought.
Conclusion and Recommendations
A tooth abscess is a serious problem that requires immediate attention. Prevention through good oral hygiene and regular dental care is the best strategy. At the first symptoms, consultation with a professional is essential to avoid complications.
Contact us
If you have any questions about what is dental a abscess or other topics, you can contact us at Channel Island Family Dental as well as our Facebook page. We look forward to your visit and we will make a timely diagnosis. Our dentists in Oxnard, Saint Paula, Venture, Newbury Park, and Port Hueneme will be able to guide you toward the best treatment to take care of your health and give you back your best smile.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Bibliography
1. Mayo Clinic. (Jun 29, 2022). Tooth abscess. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901
2. Tim Newman. (Dic 4, 2017). What’s to know about dental abscesses? Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/170136
3. Adrienne Santos-Longhurst, Christine Frank, DDS. (Feb 14, 2023) Abscessed Tooth: What You Need to Know. Healthline Media. https://www.healthline.com/health/abscessed-tooth
4. WebMD. (Nov 13, 2021). What Is an Abscessed Tooth? https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/abscessed-tooth
5. MouthHealthy. (n.d.). Abscess. https://www.mouthhealthy.org/all-topics-a-z/abscess
6. THERE IS. (Apr 8, 2022). Absceso Dental. https://ada.com/es/conditions/dental-abscess/
7. Sanders JL, Houck RC. Dental Abscess. [Updated 2023 Feb 20]. In: StatPearls [. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493149/